 |

|
||
|
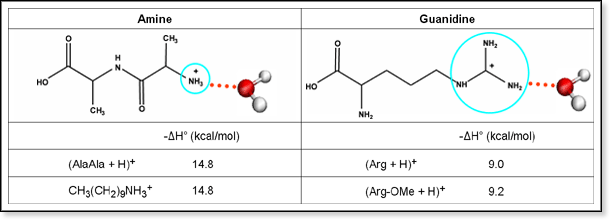
Hydration - The Role of the Charge-Carrying Group Another factor that can influence hydration is the identity of the peptide's charge-carrying group. Gas-phase peptide cations are typically protonated at the N-terminus and/or at basic amino acid residues such as arginine. Temperature-dependent equilibrium studies indicate that arginine-containing peptides have somewhat smaller water binding energies than peptides without arginine. |
||
|
|
||
 |
||