
Hydrophobicity Implications for Intrinsically Disordered Proteins
We model hydrophobicity and dewetting -- a fundamental process in which water is expelled from a surface. For example, we rapidly quantify the free energy required to dewet protein surfaces to better understand protein binding and protein folding. Read More…
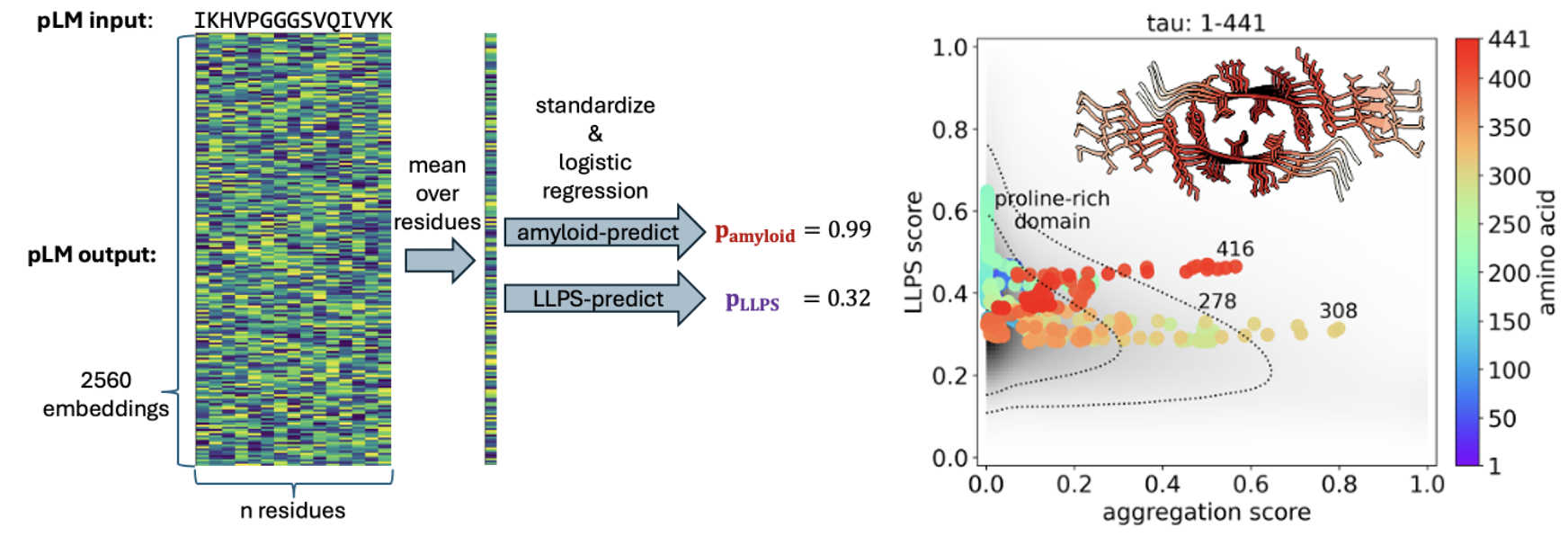
Protein Language Models
We use protein language models to predict phase separation propensities: amyloid formation and LLPS formation. We apply these models to the intrinsically disordered proteome and use them to steer peptide design.

Generating Molecules with Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning is a fundamental paradigm in machine learning that enables models to learn optimal decision-making strategies through interactions with an environment. We apply this framework to chemical language space to generate novel small molecules that bind to the alpha-synuclein aggregation-prone interface, disrupting this proteinopathy.

Cosolvent Exclusion Drives Protein Stability in TMAO and Betaine Solutions
Existing force fields miss protein–osmolyte interactions, promoting unphysical denaturation of trpcage. Our KBB force field reproduces experimental KB integrals and density. Read More…