|
Experimental
Collision Cross Sections
The
reduced mobility K0 of an ion drifting through a buffer
gas, discussed in the previous section, can be related to its collision cross section using kinetic theory.
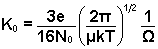
In
this expression, e is the charge on the ion, N0
the buffer gas number density at P0 and T0,
μ the reduced mass of the buffer gas
and ion, T the effective temperature, and  the momentum transfer collision integral. Thus, by measuring K0
we obtain a value for
the momentum transfer collision integral. Thus, by measuring K0
we obtain a value for  ,
an experimental "cross section". ,
an experimental "cross section".
Kinetic theory indicates that the quantity  is a momentum transfer collision integral. It is generally very difficult
to calculate theoretically, unless it is calculated for a rigid sphere,
in which case
is a momentum transfer collision integral. It is generally very difficult
to calculate theoretically, unless it is calculated for a rigid sphere,
in which case  is
equal to the projection cross section is
equal to the projection cross section  .
For a general geometrical shape the projection cross section, which is
fairly straight forward to calculate for any shape, is only an approximation
for the collision integral. .
For a general geometrical shape the projection cross section, which is
fairly straight forward to calculate for any shape, is only an approximation
for the collision integral.

However,
for similar shapes, differences between  and
and  are similar and
can be corrected for empirically. Differences between are similar and
can be corrected for empirically. Differences between  and
and  are largest (up
to 20%) for exotic geometries with large concave surfaces like bowls.
(See e.g. Shvartsburg,
A. A.; Jarrold, M. F. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 261,
86-91 and Shvartsburg,
A. A.; Schatz, G. C.; Jarrold, M. F. J. Chem. Phys. 1998,
108, 2416-2423.) are largest (up
to 20%) for exotic geometries with large concave surfaces like bowls.
(See e.g. Shvartsburg,
A. A.; Jarrold, M. F. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1996, 261,
86-91 and Shvartsburg,
A. A.; Schatz, G. C.; Jarrold, M. F. J. Chem. Phys. 1998,
108, 2416-2423.)
See also: "Theory/Analysis: Theoretical
Collision Cross Sections"
|

